事情的起因是这样的:
我买了个二自由度舵机云台,需要两路50hz的pwm,而四路电机驱动各需要3khz以下的pwm驱动,我的小车硬件设计中并没有单片机和x3pi做上下位机的设计,然而。。。。。


解决方案:
经过一番折腾,我找到了这种方法:
linux读写文件操作gpio_夏中伟的博客-CSDN博客_linux读gpio
Linux下对GPIO的操作控制(基于GPIO子系统)_金城孤客的博客-CSDN博客
当然,实现软件pwm,靠谱的定时器也不可少,于是用了享有盛名的Boost库:
C++ Boost库:计时器 timer_超级大洋葱806的博客-CSDN博客_boost timer
boost定时器使用_xiongping_的博客-CSDN博客_boost 定时器
至此,前期准备工作已经就绪
开始撸代码
我先试用了第二种,也就是system()的写法,发现运行耗时并不理想,导致pwm波形紊乱(看下图的羊癫疯)
于是我借用了技术支持徐国晟的代码(使用的是C++文件流的写法,效率超高),并在此基础上加上软件PWM封装成类的形式,方便调用,输出pwm:50HZ 占空比0.875,波形如下。
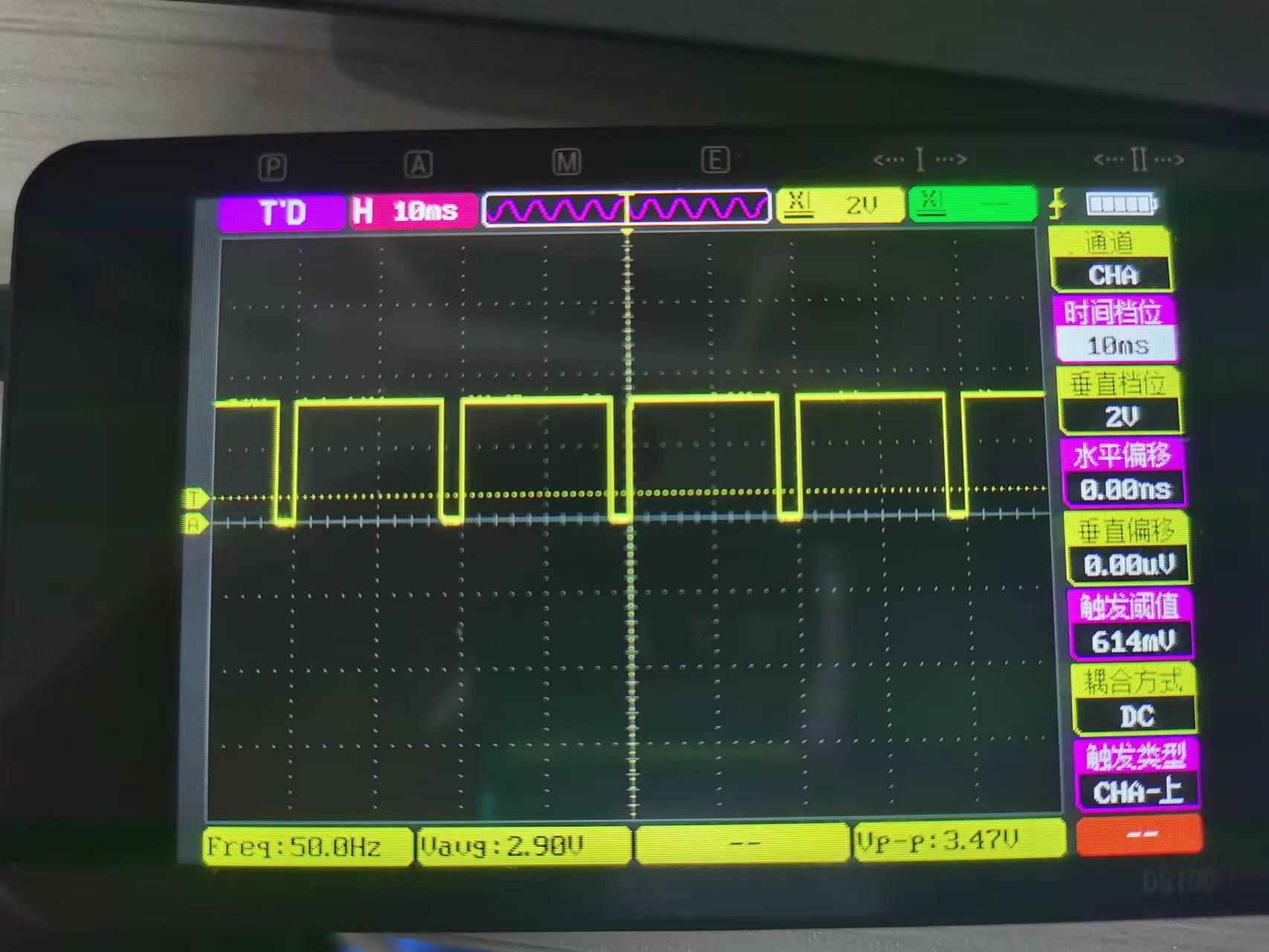
经过测试,软件PWM可以跑在3khz,足以满足我的需求。
代码展示
(本代码跑在togetherROS里)
用于声明GPIO对象的头文件gpio_40pin.h
#ifndef __GPIO_40PIN_H__
#define __GPIO_40PIN_H__
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/date_time/posix_time/posix_time.hpp>
#define SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/sys/class/gpio"
#define MAX_BUF 64
#define RET_OK 0
#define GPIO_1 NULL
#define GPIO_2 NULL
#define GPIO_3 9
#define GPIO_4 NULL
#define GPIO_5 8
#define GPIO_6 NULL
#define GPIO_7 101
#define GPIO_8 111
#define GPIO_9 NULL
#define GPIO_10 112
#define GPIO_11 6
#define GPIO_12 18
#define GPIO_13 27
#define GPIO_14 NULL
#define GPIO_15 30
#define GPIO_16 27
#define GPIO_17 NULL
#define GPIO_18 7
#define GPIO_19 12
#define GPIO_20 NULL
#define GPIO_21 13
#define GPIO_22 29
#define GPIO_23 14
#define GPIO_24 15
#define GPIO_25 NULL
#define GPIO_26 28
#define GPIO_27 106
#define GPIO_28 107
#define GPIO_29 119
#define GPIO_30 NULL
#define GPIO_31 118
#define GPIO_32 25
#define GPIO_33 4
#define GPIO_34 NULL
#define GPIO_35 103
#define GPIO_36 3
#define GPIO_37 105
#define GPIO_38 104
#define GPIO_39 NULL
#define GPIO_40 108
class gpio_40pin
{
public:
gpio_40pin();
void gpio_init(int board_num);
void gpio_set_dir(int out_flag);
void gpio_export();
void gpio_unexport();
void gpio_set_value(int value);
void gpio_get_value();
void gpio_set_edge();
void gpio_pwm(int frequency_,float Duty_ratio_);
void pwm_back();
private:
boost::asio::io_service io_;
boost::asio::deadline_timer timer_;
bool state;
int gpio;
int value_fd;
int len;
char direction_buf[MAX_BUF];
char value_buf[MAX_BUF];
int frequency;
float Duty_ratio;
int high_time;
int low_time;
};
#endif头文件gpio_40pin.h 的定义gpio_40pin.cpp
#include "gpio_rewrite/gpio_40pin.h"
gpio_40pin::gpio_40pin():timer_(io_, boost::posix_time::microseconds(10000))
{
timer_.async_wait(boost::bind(&gpio_40pin::pwm_back, this));
}
void gpio_40pin::gpio_init(int board_num)
{
gpio = board_num;
snprintf(value_buf, sizeof(value_buf), SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/gpio%d/value", gpio);
snprintf(direction_buf, sizeof(direction_buf), SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/gpio%d/direction", gpio);
}
void gpio_40pin::gpio_export()
{
char buf[MAX_BUF];
int fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/gpio%d/direction", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
close(fd);
fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/export", O_WRONLY);
len = snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", gpio);
write(fd, buf, len);
close(fd);
}else{
close(fd);
}
}
void gpio_40pin::gpio_unexport()
{
char buf[MAX_BUF];
int fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/gpio%d/direction", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
close(fd);
}else{
close(fd);
fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_DIR "/export", O_WRONLY);
len = snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", gpio);
write(fd, buf, len);
close(fd);
}
}
void gpio_40pin::gpio_set_dir(int out_flag)
{
int fd = open(direction_buf, O_WRONLY);
if (out_flag)
write(fd, "out", 4);
else
write(fd, "in", 3);
close(fd);
}
void gpio_40pin::gpio_set_value(int value)
{
int fd = open(value_buf, O_WRONLY);
if (value)
write(fd, "1", 2);
else
write(fd, "0", 2);
close(fd);
}
void gpio_40pin::pwm_back()
{
if (state == 0)
{
gpio_set_value(0);
state = 1;
timer_.expires_at(timer_.expires_at() + boost::posix_time::microseconds(low_time));
}
else
{
gpio_set_value(1);
state = 0;
timer_.expires_at(timer_.expires_at() + boost::posix_time::microseconds(high_time));
}
timer_.async_wait(boost::bind(&gpio_40pin::pwm_back, this));
}
void gpio_40pin::gpio_pwm(int frequency_,float Duty_ratio_)
{
frequency = frequency_;
Duty_ratio = Duty_ratio_;
high_time = (1000000/frequency)*Duty_ratio;
low_time = (1000000/frequency) - high_time;
printf("%d__%d\n",high_time,low_time);
io_.run();
}
//void gpio_get_value();
//void gpio_set_edge();
进行PWM测试的 time_test.cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include "gpio_rewrite/gpio_40pin.h"
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
gpio_40pin GPIO37;
GPIO37.gpio_init(GPIO_37);
GPIO37.gpio_export();
GPIO37.gpio_set_dir(1);
GPIO37.gpio_pwm(50 , 0.125);
GPIO37.gpio_unexport();
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
GPIO类分析:
先来看GPIO类的组成:
gpio_40pin():GPIO_40PIN类的构造函数。
gpio_init(int board_num):用于初始化类的文件路径并储存,进一步减少软件PWM循环中的时间消耗,输入参数board_num是X3管脚号(与GPIO1~40的管脚号不同),宏定义中已经给到了GPIO_X的定义,如例程中调用即可。
gpio_export():用于向用户空间导入GPIO操作文件。
gpio_export():用于向用户空间除去GPIO操作文件。
gpio_set_dir(int out_flag):设置GPIO输入(out_flag = 0)输出(out_flag = 1)模式。
gpio_set_value(int value):向文件写入value(0或1),也就是操作GPIO输出。
gpio_get_value():向文件读取GPIO数据。
gpio_set_edge():边沿检测。
gpio_pwm(int frequency_,float Duty_ratio_):PWM参数设定和定时器启动函数(frequency_:频率,Duty_ratio_:占空比)。
pwm_back():PWM定时回调函数。
预告:
细心的同学已经注意到了,这个工程的一部分还未完成,如io口输入和edge监测等,还有诸如pwm发生器堵塞主线程等问题,接下来我会针对这些问题更新仓库,后续给大家带来库的使用和介绍,仓库地址:https://github.com/evencewu/X3pi_GPIO_for_C ,如果对你有帮助请点个⭐,感谢捧场。
「地平线旭日X3派,开启你的嵌入式开发之旅」,欢迎正在阅读的你申请试用,一起交流开发心得