技术背景
YOLOv5是一种高效的目标检测算法,尤其在实时目标检测任务中表现突出。YOLOv5通过三种不同尺度的检测头分别处理大、中、小物体;检测头共包括三个关键任务:边界框回归、类别预测、置信度预测;每个检测头都会逐像素地使用三个Anchor,以帮助算法更准确地预测物体边界。 YOLOv5具有多种不同大小的模型(YOLOv5n、YOLOv5s、YOLOv5m、YOLOv5l、YOLOv5x)以适配不同的任务类型和硬件平台。本文以基于色选机数据集训练出的YOLOv5n模型为例,介绍如何使用PTQ进行量化编译并使用C++进行全流程的板端部署。重点介绍输入数据为RGB和NHWC时的处理方式。 本文主要提供以下几方面的指导: 1、对pytorch模型做适当的调整并导出onnx 2、以合适的方式准备校准数据并编译上板模型 3、板端部署时正确准备输入数据 4、进行反量化后处理融合以降低延时 5、提供正确的板端性能评测方法
模型输入输出说明
从pytorch导出的onnx模型,具体的输入输出信息如下图所示:
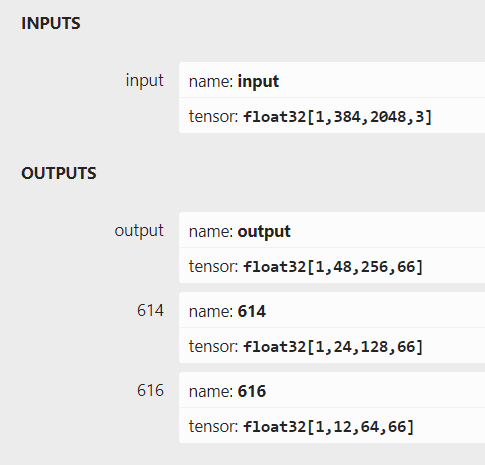
本示例使用的yolov5n模型,相较于公版在输入和输出上存在以下几点变动: 1、输入分辨率设定为384x2048,对应输出分辨率也调整为了48x256,24x128,12x64 2、类别数量设定为17,因此输出tensor的通道数变为了(17+4+1)x3=66 3、模型输入端插入了一个transpose节点,这样模型可以直接读取NHWC的输入数据
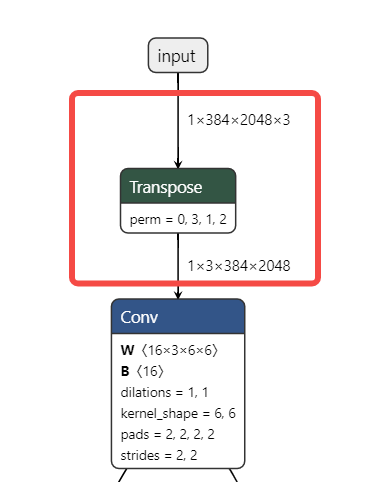
4、为了优化整体耗时,模型尾部的sigmoid计算被放在了后处理
此外本文使用的v5n模型扩充了一定参数量,介于官方的v5n和v5s之间,因此推理耗时会比普通的v5n略高。
模型导出注意事项
因为pytorch模型训练时的layout通常都是NCHW,而opencv读图之后的layout都是NHWC,因此为了部署时的预处理更加简单高效,我们建议给pytorch模型的输入节点增加一个transpose,这个transpose的作用是把NHWC转换成NCHW(对应0312的参数),从而将提供给模型的输入数据从NCHW更改为NHWC,以契合opencv读到的数据。可参考如下代码,更改后再导出onnx。
Class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
# 网络结构定义
def forward(self, x):
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# 后续网络操作
return x该模型的尾部也使用了一个transpose,让模型以NHWC的方式输出。需要强调的是,虽然模型的首尾都有transpose节点,但在编译完成后,这些transpose节点都会消失。这是因为最适配芯片的layout是NHWC,即便模型内部的算子都是NCHW排布,工具链也会转换为NHWC,这样一来模型首尾的transpose相当于不起作用,就可以被工具链干掉了,模型编译后从输入到输出全部就是NHWC。至于为什么需要手动插入transpose,这是因为工具链不想改变用户行为(即不改变onnx输入输出的layout)。如果你不加transpose,工具链可能反而会给你加上,因此建议由用户来加上transpose节点。
工具链环境
全部工程基于OE 1.2.8进行。
horizon-nn 1.1.0
horizon_tc_ui 1.24.3
hbdk 3.49.15PTQ量化编译流程
准备校准数据

先准备100张如上图所示的色选机数据集图片存放在seed100文件夹,之后可借助horizon_model_convert_sample的02_preprocess.sh脚本帮助我们生成校准数据。 02_preprocess.sh
python3 ../../../data_preprocess.py \
--src_dir ./seed100 \
--dst_dir ./calibration_data_rgb_f32 \
--pic_ext .rgb \
--read_mode opencv \
--saved_data_type float32preprocess.py
def calibration_transformers():
transformers = [
PadResizeTransformer(target_size=(384, 2048)),
BGR2RGBTransformer(data_format="HWC"),
]
return transformers校准数据仅需resize成符合模型输入的尺寸,并按照HWC转换成RGB即可。
配置yaml文件
model_parameters:
onnx_model: 'yolov5n-rgb.onnx'
march: 'bayes-e'
working_dir: 'model_output'
output_model_file_prefix: 'yolov5n-rgb'
input_parameters:
input_type_rt: 'rgb'
input_layout_rt: 'NHWC'
input_type_train: 'rgb'
input_layout_train: 'NHWC'
norm_type: 'data_scale'
scale_value: 0.003921568627451
calibration_parameters:
cal_data_dir: './calibration_data_rgb_f32'
cal_data_type: 'float32'
calibration_type: 'default'
compiler_parameters:
optimize_level: 'O3'input_type_rt指模型在部署时输入的数据类型,这里使用rgb input_layout_rt指模型在部署时输入的数据排布,由于rgb本身就是NHWC,且为了简化预处理,这里使用NHWC input_type_train指浮点模型训练时使用的数据类型,这里使用rgb input_layout_train指浮点模型训练时使用的数据排布,虽然pytorch原生是NCHW,但由于我们在输入处插入了transpose节点,因此这里使用NHWC norm_type和scale_value根据浮点模型训练时使用的归一化参数设置,这里配置scale为1/255(mean和scale的具体计算方法可参考文章 https://developer.d-robotics.cc/forumDetail/71036815603174578)
编译上板模型
hb_mapper makertbin --config ./yolov5n_config.yaml --model-type onnx执行以上命令后,即可编译出用于板端部署的bin模型。
=============================================================================
Output Cosine Similarity L1 Distance L2 Distance Chebyshev Distance
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
output 0.996515 0.254891 0.000449 6.486392
614 0.997272 0.258633 0.000823 9.011304
616 0.995311 0.306030 0.002021 3.344787根据编译日志可看出,yolov5n模型的三个输出头,量化前后的余弦相似度均>0.99,符合精度要求。
Runtime部署流程
在算法工具链的交付包中,ai benchmark示例包含了读图、前处理、推理、后处理等完整流程的C++源码,但考虑到ai benchmark代码耦合度较高,有不低的学习成本,不方便用户嵌入到自己的工程应用中,因此我们提供了基于horizon_runtime_sample示例修改的简易版本C++代码,只包含1个头文件和1个C++源码,用户仅需替换原有的00_quick_start示例即可编译运行。 通常来说,模型编译完成后,尾部会有CPU计算的反量化节点。一个常见的优化策略是将反量化计算和后处理一起运行,节约一遍数据遍历次数,从而降低耗时。本文同时提供了不删除反量化算子和删除反量化算子的后处理代码示例。反量化融合的具体原理和实践参考可以阅读这篇文章: https://developer.d-robotics.cc/forumDetail/116476291842200072
头文件
该头文件内容主要来自于ai benchmark的code/include/base/perception_common.h头文件,包含了对argmax和计时功能的定义,以及目标检测任务相关结构体的定义。
#include <chrono>
typedef std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point Time;
typedef std::chrono::duration<u_int64_t, std::micro> Micro;
template <class ForwardIterator>
inline size_t argmax(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last) {
return std::distance(first, std::max_element(first, last));
}
typedef struct Bbox {
float xmin{0.0};
float ymin{0.0};
float xmax{0.0};
float ymax{0.0};
Bbox() {}
Bbox(float xmin, float ymin, float xmax, float ymax)
: xmin(xmin), ymin(ymin), xmax(xmax), ymax(ymax) {}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Bbox &bbox) {
const auto precision = os.precision();
const auto flags = os.flags();
os << "[" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(6) << bbox.xmin << ","
<< bbox.ymin << "," << bbox.xmax << "," << bbox.ymax << "]";
os.flags(flags);
os.precision(precision);
return os;
}
~Bbox() {}
} Bbox;
typedef struct Detection {
int id{0};
float score{0.0};
Bbox bbox;
const char *class_name{nullptr};
Detection() {}
Detection(int id, float score, Bbox bbox)
: id(id), score(score), bbox(bbox) {}
Detection(int id, float score, Bbox bbox, const char *class_name)
: id(id), score(score), bbox(bbox), class_name(class_name) {}
friend bool operator>(const Detection &lhs, const Detection &rhs) {
return (lhs.score > rhs.score);
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Detection &det) {
const auto precision = os.precision();
const auto flags = os.flags();
os << "{"
<< R"("bbox")"
<< ":" << det.bbox << ","
<< R"("prob")"
<< ":" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(6) << det.score << ","
<< R"("label")"
<< ":" << det.id << ","
<< R"("class_name")"
<< ":\"" << det.class_name << "\"}";
os.flags(flags);
os.precision(precision);
return os;
}
~Detection() {}
} Detection;
struct Perception {
std::vector<Detection> det;
enum {
DET = (1 << 0),
} type;
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, Perception &perception) {
os << "[";
if (perception.type == Perception::DET) {
auto &detection = perception.det;
for (int i = 0; i < detection.size(); i++) {
if (i != 0) {
os << ",";
}
os << detection[i];
}
}
os << "]";
return os;
}
};源码
为方便用户阅读,该源码使用全局变量定义了若干参数,请用户在实际的应用工程中,避免使用过多全局变量。代码中已在合适的位置添加中文注释。需要特意说明的是,置信度阈值使用了score_threshold_objness和score_threshold两个变量,第一个需要设置成经过sigmoid反函数的值,比如原来设置的0.1,那么sigmoid经过反函数以后的值大概是-2.3,这样设置可以大大降低后处理的时间,第二个变量则是正常的置信度阈值,通常二选一即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <algorithm>
#include "dnn/hb_dnn.h"
#include "opencv2/core/mat.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "head.h"
//上板模型的路径
//auto modelFileName = "yolov5s-ori.bin";
auto modelFileName = "yolov5s-ori_modified.bin";
// 单张测试图片的路径
std::string imagePath = "1.png";
// 测试图片的宽度
int image_width = 2048;
// 测试图片的高度
int image_height = 384;
// 置信度阈值
float score_threshold_objness = -2.3;
float score_threshold = 0.1;
// 分类目标数
int num_classes = 17;
// 每个Anchor对应的输出通道数
int num_pred = num_classes + 4 + 1;
// nms的topk
int nms_top_k = 5000;
// nms的iou阈值
float nms_iou_threshold = 0.2;
// 为模型推理准备输入输出内存空间
void prepare_tensor(int input_count,
int output_count,
hbDNNTensor *input_tensor,
hbDNNTensor *output_tensor,
hbDNNHandle_t dnn_handle) {
hbDNNTensor *input = input_tensor;
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; i++) {
hbDNNGetInputTensorProperties(&input[i].properties, dnn_handle, i);
int input_memSize = input[i].properties.alignedByteSize;
hbSysAllocCachedMem(&input[i].sysMem[0], input_memSize);
input[i].properties.alignedShape = input[i].properties.validShape;
}
hbDNNTensor *output = output_tensor;
for (int i = 0; i < output_count; i++) {
hbDNNGetOutputTensorProperties(&output[i].properties, dnn_handle, i);
int output_memSize = output[i].properties.alignedByteSize;
hbSysAllocCachedMem(&output[i].sysMem[0], output_memSize);
}
}
// 读取bgr图片并转换为特定格式再存储进输入内存
void read_image_2_tensor_as_rgb(std::string imagePath,
hbDNNTensor *input_tensor) {
hbDNNTensor *input = input_tensor;
hbDNNTensorProperties Properties = input->properties;
cv::Mat bgr_mat = cv::imread(imagePath, cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
cv::Mat rgb_mat;
cv::cvtColor(bgr_mat, rgb_mat, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
auto input_data = input->sysMem[0].virAddr;
uint8_t *rgb_data = rgb_mat.ptr<uint8_t>();
int image_length = 384 * 2048 * 3;
memcpy(input_data, rgb_data, image_length);
Time preprocess_start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
uint8_t *data_u8{reinterpret_cast<uint8_t *>(input_data)};
int8_t *data_s8{reinterpret_cast<int8_t *>(input_data)};
for (int i = 0; i < image_length; i++)
data_s8[i] = data_u8[i] - 128;
Time preprocess_end = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
Micro preprocess_latency = std::chrono::duration_cast<Micro>(preprocess_end - preprocess_start);
std::cout << "preprocess -128 time: " << static_cast<float>(preprocess_latency.count() / 1000.0) << " ms" << std::endl;
}
float dequantiScale(int32_t data, bool big_endian, float &scale_value) {
return static_cast<float>(r_int32(data, big_endian)) * scale_value;
}
// 后处理的核心代码(不包括nms),初步筛选检测框
void process_tensor_core(hbDNNTensor *tensor,
int layer,
std::vector<Detection> &dets){
hbSysFlushMem(&(tensor->sysMem[0]), HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_INVALIDATE);
int height, width, stride;
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> anchors;
if(layer == 0){
height = 48; width = 256; stride = 8; anchors = {{10, 13}, {16, 30}, {33, 23}};
} else if (layer == 1){
height = 24; width = 128; stride = 16; anchors = {{30, 61}, {62, 45}, {59, 119}};
} else if (layer == 2){
height = 12; width = 64; stride = 32; anchors = {{116, 90}, {156, 198}, {373, 326}};
}
int anchor_num = anchors.size();
auto quanti_type = tensor->properties.quantiType;
if(quanti_type == hbDNNQuantiType::NONE){
auto *data = reinterpret_cast<float *>(tensor->sysMem[0].virAddr);
for (uint32_t h = 0; h < height; h++) {
for (uint32_t w = 0; w < width; w++) {
for (int k = 0; k < anchor_num; k++) {
double anchor_x = anchors[k].first;
double anchor_y = anchors[k].second;
float *cur_data = data + k * num_pred;
float objness = cur_data[4];
if(objness < score_threshold_objness)
continue;
int id = argmax(cur_data + 5, cur_data + 5 + num_classes);
double x1 = 1 / (1 + std::exp(-objness)) * 1;
double x2 = 1 / (1 + std::exp(-cur_data[id + 5]));
double confidence = x1 * x2;
if (confidence < score_threshold)
continue;
float center_x = cur_data[0];
float center_y = cur_data[1];
float scale_x = cur_data[2];
float scale_y = cur_data[3];
double box_center_x =
((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-center_x))) * 2 - 0.5 + w) * stride;
double box_center_y =
((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-center_y))) * 2 - 0.5 + h) * stride;
double box_scale_x =
std::pow((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-scale_x))) * 2, 2) * anchor_x;
double box_scale_y =
std::pow((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-scale_y))) * 2, 2) * anchor_y;
double xmin = (box_center_x - box_scale_x / 2.0);
double ymin = (box_center_y - box_scale_y / 2.0);
double xmax = (box_center_x + box_scale_x / 2.0);
double ymax = (box_center_y + box_scale_y / 2.0);
double xmin_org = xmin;
double xmax_org = xmax;
double ymin_org = ymin;
double ymax_org = ymax;
if (xmax_org <= 0 || ymax_org <= 0)
continue;
if (xmin_org > xmax_org || ymin_org > ymax_org)
continue;
xmin_org = std::max(xmin_org, 0.0);
xmax_org = std::min(xmax_org, image_width - 1.0);
ymin_org = std::max(ymin_org, 0.0);
ymax_org = std::min(ymax_org, image_height - 1.0);
Bbox bbox(xmin_org, ymin_org, xmax_org, ymax_org);
dets.emplace_back((int)id, confidence, bbox);
}
data = data + num_pred * anchors.size();
}
}
} else if(quanti_type == hbDNNQuantiType::SCALE){
auto *data = reinterpret_cast<int32_t *>(tensor->sysMem[0].virAddr);
auto dequantize_scale_ptr = tensor->properties.scale.scaleData;
bool big_endian = false;
for (uint32_t h = 0; h < height; h++) {
for (uint32_t w = 0; w < width; w++) {
for (int k = 0; k < anchor_num; k++) {
double anchor_x = anchors[k].first;
double anchor_y = anchors[k].second;
int32_t *cur_data = data + k * num_pred;
int offset = num_pred * k;
float objness = dequantiScale(cur_data[4], big_endian, *(dequantize_scale_ptr+offset+4));
if (objness < score_threshold_objness)
continue;
double max_cls_data = std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest();
int id{0};
for (int cls = 0; cls < num_classes; cls += 4) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
float score = cur_data[cls + 5 + j] * dequantize_scale_ptr[offset+cls+5+j];
if (score > max_cls_data) {
max_cls_data = score;
id = cls + j;
}
}
}
double x1 = 1 / (1 + std::exp(-objness)) * 1;
double x2 = 1 / (1 + std::exp(-max_cls_data));
double confidence = x1 * x2;
float center_x = dequantiScale(
cur_data[0], big_endian, *(dequantize_scale_ptr + offset));
float center_y = dequantiScale(
cur_data[1], big_endian, *(dequantize_scale_ptr + offset + 1));
float scale_x = dequantiScale(
cur_data[2], big_endian, *(dequantize_scale_ptr + offset + 2));
float scale_y = dequantiScale(
cur_data[3], big_endian, *(dequantize_scale_ptr + offset + 3));
double box_center_x =
((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-center_x))) * 2 - 0.5 + w) * stride;
double box_center_y =
((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-center_y))) * 2 - 0.5 + h) * stride;
double box_scale_x =
std::pow((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-scale_x))) * 2, 2) * anchor_x;
double box_scale_y =
std::pow((1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-scale_y))) * 2, 2) * anchor_y;
double xmin = (box_center_x - box_scale_x / 2.0);
double ymin = (box_center_y - box_scale_y / 2.0);
double xmax = (box_center_x + box_scale_x / 2.0);
double ymax = (box_center_y + box_scale_y / 2.0);
double xmin_org = xmin;
double xmax_org = xmax;
double ymin_org = ymin;
double ymax_org = ymax;
if (xmax_org <= 0 || ymax_org <= 0)
continue;
if (xmin_org > xmax_org || ymin_org > ymax_org)
continue;
xmin_org = std::max(xmin_org, 0.0);
xmax_org = std::min(xmax_org, image_width - 1.0);
ymin_org = std::max(ymin_org, 0.0);
ymax_org = std::min(ymax_org, image_height - 1.0);
Bbox bbox(xmin_org, ymin_org, xmax_org, ymax_org);
dets.emplace_back((int)id, confidence, bbox);
}
data = data + num_pred * anchors.size() + 2;
}
}
} else {
std::cout << "x5 unsupport shift dequantize!" << std::endl;
}
}
// nms处理,精挑细选出合适的检测框
void yolo5_nms(std::vector<Detection> &input,
std::vector<int>& indices,
std::vector<Detection> &result) {
std::sort(input.begin(), input.end(), std::greater<Detection>());
//std::cout<<"before nms size: "<<input.size()<<std::endl;
std::vector<float> areas;
areas.reserve(input.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < input.size(); i++) {
float width = input[i].bbox.xmax - input[i].bbox.xmin;
float height = input[i].bbox.ymax - input[i].bbox.ymin;
areas.push_back(width * height);
}
indices.clear();
float area_intersection;
for (size_t i = 0; i < input.size(); ++i) {
bool keep = true;
for (int k = (int)indices.size()-1; k >= 0 && keep; --k) {
int kept_idx = indices[k];
float xx1 = std::max(input[i].bbox.xmin, input[kept_idx].bbox.xmin);
float yy1 = std::max(input[i].bbox.ymin, input[kept_idx].bbox.ymin);
float xx2 = std::min(input[i].bbox.xmax, input[kept_idx].bbox.xmax);
float yy2 = std::min(input[i].bbox.ymax, input[kept_idx].bbox.ymax);
if ((xx2 > xx1) && (yy2 > yy1)) {
area_intersection = (xx2 - xx1) * (yy2 - yy1);
keep = area_intersection <= nms_iou_threshold * (areas[i] + areas[kept_idx] - area_intersection);
}
}
if (keep) {
indices.push_back(i);
result.push_back(input[i]);
//std::cout << "score " << input[i].score;
//std::cout << " xmin " << input[i].bbox.xmin;
//std::cout << " ymin " << input[i].bbox.ymin;
//std::cout << " xmax " << input[i].bbox.xmax;
//std::cout << " ymax " << input[i].bbox.ymax << std::endl;
}
}
//std::cout << "after nms size: " << indices.size() << std::endl;
}
// 多线程加速后处理计算
std::mutex dets_mutex;
void process_tensor_thread(hbDNNTensor *tensor, int layer, std::vector<Detection> &dets){
std::vector<Detection> local_dets;
process_tensor_core(tensor, layer, local_dets);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(dets_mutex);
dets.insert(dets.end(), local_dets.begin(), local_dets.end());
}
void post_process(std::vector<hbDNNTensor> &tensors,
Perception *perception,
std::vector<int>& indices){
perception->type = Perception::DET;
std::vector<Detection> dets;
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < tensors.size(); ++i) {
threads.emplace_back([&tensors, i, &dets](){
process_tensor_thread(&tensors[i], i, dets);
});
}
for (auto &thread : threads)
thread.join();
yolo5_nms(dets, indices, perception->det);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
//初始化模型
hbPackedDNNHandle_t packed_dnn_handle;
hbDNNHandle_t dnn_handle;
const char **model_name_list;
int model_count = 0;
hbDNNInitializeFromFiles(&packed_dnn_handle, &modelFileName, 1);
hbDNNGetModelNameList(&model_name_list, &model_count, packed_dnn_handle);
hbDNNGetModelHandle(&dnn_handle, packed_dnn_handle, model_name_list[0]);
std::cout<< "yolov5 demo begin!" << std::endl;
std::cout<< "load model success" <<std::endl;
//获取模型输入输出分支数
int input_count = 0;
int output_count = 0;
hbDNNGetInputCount(&input_count, dnn_handle);
hbDNNGetOutputCount(&output_count, dnn_handle);
std::vector<hbDNNTensor> input_tensors;
std::vector<hbDNNTensor> output_tensors;
input_tensors.resize(input_count);
output_tensors.resize(output_count);
prepare_tensor(input_count, output_count, input_tensors.data(), output_tensors.data(), dnn_handle);
std::cout<< "prepare intput and output tensor success" << std::endl;
read_image_2_tensor_as_rgb(imagePath, input_tensors.data());
std::cout<< "read image to tensor as rgb success" << std::endl;
//推理模型并计时
hbDNNTaskHandle_t task_handle = nullptr;
hbDNNTensor *output = output_tensors.data();
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
hbSysFlushMem(&input_tensors[i].sysMem[0], HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_CLEAN);
hbDNNInferCtrlParam infer_ctrl_param;
HB_DNN_INITIALIZE_INFER_CTRL_PARAM(&infer_ctrl_param);
Time infer_start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
hbDNNInfer(&task_handle,
&output,
input_tensors.data(),
dnn_handle,
&infer_ctrl_param);
hbDNNWaitTaskDone(task_handle, 0);
Time infer_end = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
Micro infer_latency = std::chrono::duration_cast<Micro>(infer_end - infer_start);
std::cout << "model infer time: " << static_cast<float>(infer_latency.count() / 1000.0) << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout<< "model infer success" << std::endl;
//后处理并计时
Time postprocess_start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto perception = std::shared_ptr<Perception>(new Perception);
std::vector<int> indices;
indices.reserve(1000);
post_process(output_tensors, perception.get(), indices);
Time postprocess_end = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
Micro postprocess_latency = std::chrono::duration_cast<Micro>(postprocess_end - postprocess_start);
std::cout << "postprocess time: " << static_cast<float>(postprocess_latency.count() / 1000.0) << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "postprocess success" << std::endl;
cv::Mat image = cv::imread(imagePath);
for(int i = 0; i < perception->det.size(); i++){
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Point(perception->det[i].bbox.xmin, perception->det[i].bbox.ymin),
cv::Point(perception->det[i].bbox.xmax, perception->det[i].bbox.ymax), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
cv::imwrite("output.jpg", image);
//释放任务占用的资源
hbDNNReleaseTask(task_handle);
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
hbSysFreeMem(&(input_tensors[i].sysMem[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < output_count; i++)
hbSysFreeMem(&(output_tensors[i].sysMem[0]));
hbDNNRelease(packed_dnn_handle);
std::cout<< "release resources success" << std::endl;
std::cout<< "yolov5 demo end!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}这里强调一下read_image_2_tensor_as_rgb函数:由于input_type_rt配置为rgb/bgr时,板端模型的输入是int8,而不是uint8,在X5平台,需要用户在预处理中遍历所有输入数据手动做-128处理,未来的工具链版本会针对RGB输入场景做更多的适配,以避免这种额外操作。
运行说明
用户可将头文件和源码放入horizon_runtime_sample/code/00_quick_start/src路径,并执行build_x5.sh编译工程,再将horizon_runtime_sample/x5文件夹复制到开发板的/userdata目录,并在/userdata/x5/script/00_quick_start/路径下存放上板模型、测试图片等文件,并编写板端运行脚本:
bin=../aarch64/bin/run_mobileNetV1_224x224
lib=../aarch64/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${lib}:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export BMEM_CACHEABLE=true
${bin} 运行结果如下(以未删除反量化的模型为例):
yolov5 demo begin!
load model success
prepare intput and output tensor success
preprocess -128 time: 0.769 ms
read image to tensor as rgb success
model infer time: 9.669 ms
model infer success
score 0.585894 xmin 1448.85 ymin 148.522 xmax 1516.65 ymax 276.543
postprocess time: 1.574 ms
postprocess success
release resources success
yolov5 demo end!对于这次推理,我们的输入图像为下图:

可以看到,推理程序成功识别到了目标物体,并且给出了正确的坐标信息:
score 0.585894 xmin 1448.85 ymin 148.522 xmax 1516.65 ymax 276.543模型推理耗时说明
需要强调的是,应用程序在推理第一帧的时候,会产生加载推理框架导致的额外耗时,因此运行该程序测出的模型推理耗时是偏高的。准确的模型推理时间应当以hrt_model_exec工具实测结果为准,参考命令: hrt_model_exec perf --model-file ./yolov5n.bin --thread-num 1(测试单线程单帧延时,关注latency) hrt_model_exec perf --model-file ./yolov5n.bin --thread-num 8(测试多线程极限吞吐量,关注FPS)